

Vertebrates, like humans, only practice sexual reproduction. It includes the generation of gametes, which have half as many chromosomes as the organism’s other cells Each has benefits and drawbacks of its own. It is important to know that asexual reproduction is considerably simpler than sexual reproduction. Among the Apicomplexa, binary fission is used to describe the division. Reproduction can be divided into two categories: sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. Binary fission is defined as the formation of two daughter cells per division round. It also plays a role in evolution as well as ensuring the survival of the species. Reproduction is a natural rule that applies to all living things, including people, animals, plants, algae, fungi, and other microbes. ISRO CS Syllabus for Scientist/Engineer Exam.Simple cell division in single-celled organisms. The process in which a parent cell splits into two daughter cells of approximately equal size. ISRO CS Original Papers and Official Keys Definition: Search for: Biology Glossary search by.GATE CS Original Papers and Official Keys.DevOps Engineering - Planning to Production Definition: A common type of asexual reproduction in prokaryotes like bacteria, where a parent cell divides to form two identical cells and each having the. How exactly does binary fission work Well, three steps must be completed for a parent cell to split in two: To split into two daughter cells a parent cell undergoes binary fission.Python Backend Development with Django(Live).
#Binary fission definition in biology android
Android App Development with Kotlin(Live).
#Binary fission definition in biology full
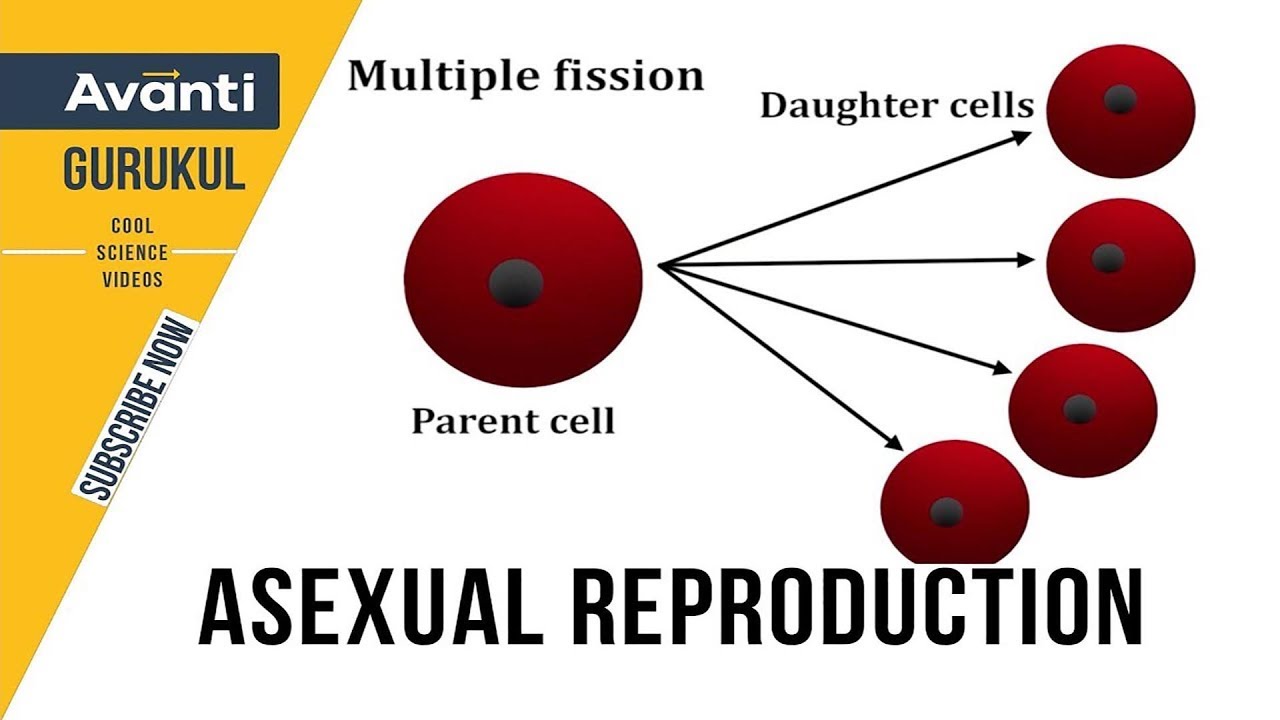
Data Structures & Algorithms in JavaScript.Data Structure & Algorithm Classes (Live).The term binary fission is frequently used, incorrectly, to refer to the division of unicellular eukaryotes, but strictly speaking, the term should only be applied to prokaryotes. The septal ring proteins, which collect around the equatorial site of division, control this process. The actual physical division of the cell into two compartments occurs when the cell wall and cell membrane grow inward to form a wall ("division septum") across the middle of the cell. As the cell stretches out during division, the two chromosomes move apart, and one passes into each of the two daughter cells. Each chromosome then affixes itself to the cell membrane. DNA polymerase converts each of these single strands of DNA into double strands and, ultimately, two circular chromosomes are produced. As the bubble gets larger and larger, the separated chromosome strands become longer and longer. There is normally a single origin of replication in prokaryotes, not multiple ones as is the case in eukaryotes. This process starts when a replication bubble opens in the DNA of the chromosome.
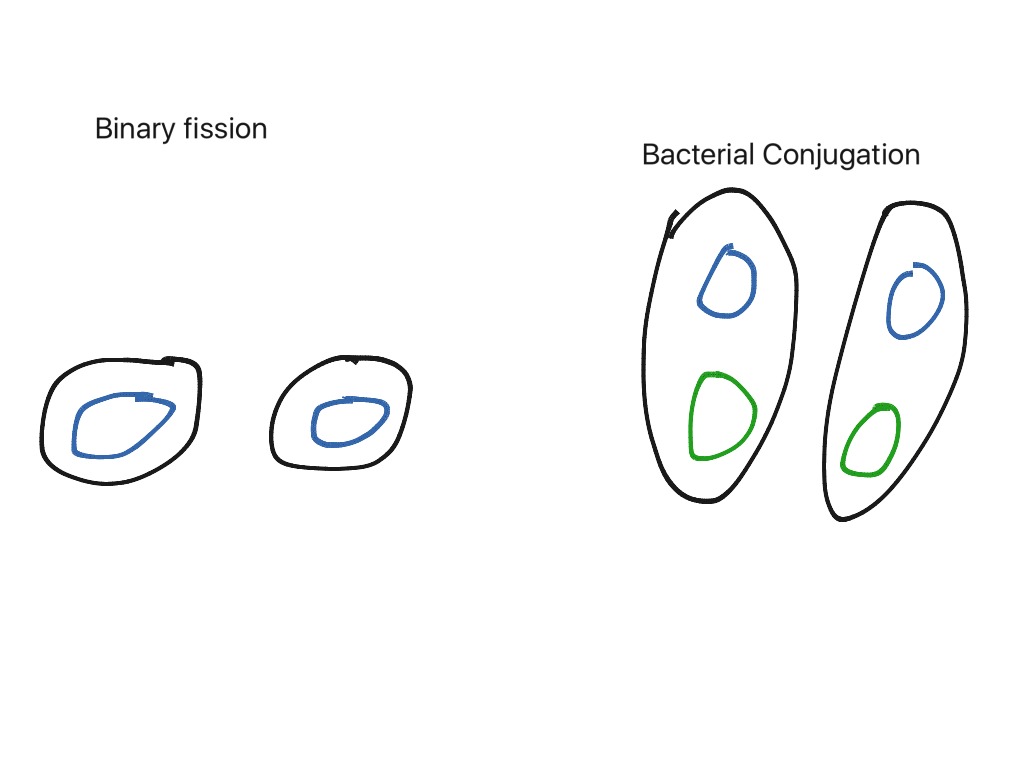
Or it can occur via either of the two more complex processes, meiosis and mitosis, characteristic of eukaryotes.īefore fission can occur, the cell must replicate its chromosome, which is circular. Although this form of reproduction is asexual, it is not the same as vegetative reproduction, a process occurring only in eukaryotes that depends on the mitotic reproduction of cells.Ĭell division (above) can be a matter of simple fission, as described on this page, which occurs only in prokaryotes. But each daughter cell does contain a complete copy of the parental chromosome. This method of cellular reproduction occurs only in prokaryotes ( bacteria and archaeans), although it is true that some organelles of eukaryotic cells, such as the mitochondria reproduce themselves by this method.Īs one might expect, the volume of the two daughter cells produced is initially half that of the parent cell before the division. Binary fission is the asexual reproduction of a cell, without mitosis or meiosis, by division into two approximately equal parts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
